Round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium
You will find that lithium-ion batteries usually deliver higher round trip efficiency than flow batteries, with recent data showing lithium-ion batteries often exceed 90%. Round trip efficiency measures how much energy you can recover after charging and discharging a battery. This metric plays a key role in deciding which technology best supports renewable energy and grid storage. Comparing the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium helps you understand which system minimizes energy losses and improves overall economic results.
-
Higher round-trip efficiency means less wasted energy and better environmental performance for grid-connected storage.
-
Lithium-ion batteries excel in frequent energy cycling due to their superior efficiency.
Key Takeaways
-
Lithium-ion batteries typically achieve over 90% round trip efficiency, meaning they waste less energy during charging and discharging.
-
Flow batteries, while having lower efficiency (65% to 85%), offer long lifespans and stable performance, making them suitable for long-term energy storage.
-
Choosing a battery with higher round trip efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and reduced energy waste, benefiting both the environment and your wallet.
-
Consider your specific energy needs: lithium-ion batteries excel in rapid cycling, while flow batteries are ideal for long-duration storage.
-
Always check the round trip efficiency rating before purchasing a battery system to ensure you maximize energy recovery and minimize operational costs.
Round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium
Direct efficiency comparison
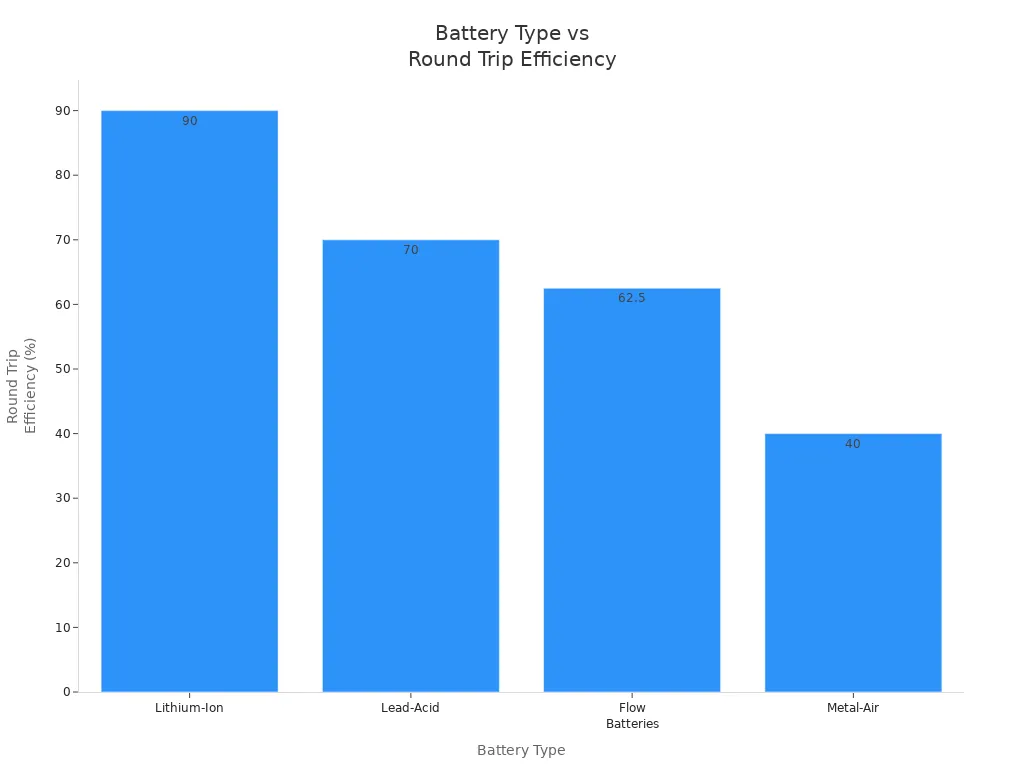
When you compare the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium, you see clear differences in how each technology performs. Lithium-ion batteries usually achieve higher round trip efficiency, often exceeding 90%. Flow batteries typically reach between 65% and 85%. This means lithium-ion batteries waste less energy during charging and discharging. You can see these differences in the table below:
|
Battery Type |
Round Trip Efficiency (RTE) |
Energy Loss Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
|
Lithium-Ion |
90%+ |
Low energy loss, efficient design |
|
Flow Batteries |
65%–85% |
Energy loss from heat and side reactions |
|
Lead-Acid |
~70% |
Higher losses due to internal resistance |
|
Metal-Air |
as low as 40% |
Significant energy loss due to chemical reactions |
Tip: Higher round trip efficiency means you get more usable energy from every charge. This helps you save money and reduce waste.
You can also visualize the differences in round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium using the chart below:
Typical efficiency ranges
You will find that the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium depends on several factors, including battery chemistry, design, and operating conditions. Lithium-ion batteries usually deliver round trip efficiency values between 85% and 95%. Many studies report system-level efficiency targets for lithium-ion batteries at about 85%. Some research identifies 86% as a typical value.
Flow batteries show more variation. Most flow batteries reach round trip efficiency values from 65% to 85%. Some advanced designs report stack charging efficiencies up to 95% under certain conditions, such as mid-load and specific states of charge. However, most real-world systems operate in the 70% to 80% range.
-
Typical round trip efficiency values for lithium-ion batteries:
-
Around 85% to 86%
-
System-level targets at about 85%
-
-
Typical round trip efficiency values for flow batteries:
-
65% to 85% in most cases
-
Some stack charging efficiencies up to 95% under ideal conditions
-
You should remember that the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium affects how much energy you can actually use after charging. Higher efficiency means better performance and lower costs over time.
Note: Factors like temperature, cycle life, and charging rates can change the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium. You need to consider these when choosing a battery for your needs.
Flow batteries offer benefits beyond efficiency. They last 20 years or more, use recyclable materials, and provide safe, stable operation. Their modular design lets you scale up storage for large projects. Lithium-ion batteries excel in efficiency and work well for frequent cycling and rapid charging.
By understanding the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium, you can make better decisions for energy storage. You will know which technology fits your needs, whether you want high efficiency or long-term durability.
Definition and calculation
You need to understand round trip efficiency if you want to compare battery technologies. This metric shows how well a battery stores and releases energy. When you charge a battery, some energy gets lost. Round trip efficiency tells you how much energy you actually get back after charging and discharging.
-
Round trip efficiency measures the effectiveness of energy storage and release.
-
You calculate it using this formula:
Energy Output ÷ Energy Input × 100 = Round Trip Efficiency (%) -
For example, if you put 10 kWh into a battery and get 8 kWh back, the round trip efficiency is 80%.
Here is a simple table to help you visualize the calculation:
|
Energy Input (kWh) |
Energy Output (kWh) |
Round Trip Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
10 |
8 |
80 |
|
100 |
90 |
90 |
Tip: Higher round trip efficiency means less energy wasted and more savings for you.
Why efficiency matters
You should care about round trip efficiency because it affects your costs and the environment. When you choose a battery for your home, business, or the grid, higher efficiency means you need less energy to get the same amount of power. This lowers your electricity bills and helps reduce resource use.
-
Round trip efficiency impacts economic viability and sustainability.
-
Higher efficiency reduces energy input, lowering operational expenses.
-
Efficient batteries help stabilize the grid and support renewable energy.
-
Better efficiency means improved return on investment.
If you compare the round trip efficiency of flow battery vs. lithium, you see how this metric influences your choice. Efficient batteries make renewable energy more practical and affordable. You can help the environment and save money by choosing systems with high round trip efficiency.
Note: Efficiency is a key factor in long-term energy planning and grid stability.
Flow battery efficiency factors
Chemistry and design
You will find that the chemistry and design of a flow battery play a big role in its round trip efficiency. Vanadium redox flow batteries stand out in the market. Their unique chemistry prevents cross-contamination between electrolytes. This feature helps maintain high efficiency and long-term stability. Vanadium offers several oxidation states and a wide electrochemical voltage window. These qualities boost both efficiency and durability.
-
Vanadium redox flow batteries dominate commercial use.
-
Their chemistry supports long cycle lives, often reaching 15,000 to 20,000 cycles.
-
The design allows for easy scaling, making them ideal for large energy storage projects.
You should also know that round trip efficiency is not the only important metric. Power density and energy density matter, too. The chemistry and design you choose will affect all these factors.
Operating conditions
Operating conditions can change how well your flow battery performs. Temperature, flow rate, and state of charge all influence efficiency. If you keep the battery within its recommended temperature range, you will see better results. High or low temperatures can increase energy losses.
You should monitor the flow rate of the electrolyte. If the flow is too slow or too fast, efficiency drops. Keeping the battery at an optimal state of charge also helps maintain high performance. Regular checks and proper management ensure you get the most from your system.
Tip: Consistent operating conditions help you achieve stable and reliable efficiency from your flow battery.
Degradation and lifespan
Degradation affects every battery, but flow batteries handle it better than many other types. Over time, you may notice capacity fade, which means the battery holds less energy. This reduces efficiency and can raise operational costs. Internal resistance may also increase, making charging slower and less effective.
-
Flow batteries usually degrade at a rate of 1–2% per year.
-
You can use deeper discharge cycles without losing much capacity.
-
Lower degradation rates mean longer lifespans and more reliable performance.
With proper care, your flow battery can last for decades. This long lifespan makes flow batteries a strong choice for projects that need stable, long-term energy storage.
Lithium-ion battery efficiency factors
Chemistry and design
You will notice that the chemistry and design of lithium-ion batteries play a big role in their round trip efficiency. Different chemistries, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) or lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), affect how much energy you can recover after charging. The way manufacturers design the cells also changes how efficiently the battery works.
-
Fewer lithium ions available for conversion between charged and uncharged states allow for quicker charging and use less energy.
-
Internal resistance increases when deposits form on the electrodes, which causes more energy to be lost as heat during charging and discharging.
You should look for batteries with advanced cell designs and high-quality materials. These features help keep internal resistance low and improve efficiency.
Cycle life and degradation
Lithium-ion batteries lose efficiency as they age. Each time you charge and discharge the battery, the materials inside wear down a little. This process is called degradation. Over time, the battery holds less energy and becomes less efficient.
-
As the cycle life increases, you will see both capacity fade and a drop in energy efficiency.
-
The round trip efficiency can start at about 90% but may fall to 75% by the end of the battery’s life.
You can slow down this decline by avoiding deep discharges and keeping the battery at moderate temperatures. Regular maintenance and smart charging habits help extend the useful life of your battery.
Environmental impact
You should consider the environmental impact when choosing lithium-ion batteries. These batteries use metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. Mining and processing these materials can affect the environment. Recycling programs help reduce waste and recover valuable materials, but not all batteries get recycled.
Tip: Choose batteries from manufacturers that support recycling and use responsible sourcing for raw materials. This helps lower the environmental footprint of your energy storage system.
Lithium-ion batteries offer high efficiency and strong performance, but you need to balance these benefits with their environmental effects.
Real-world performance
Lab vs. field data
You may notice that battery efficiency numbers often look higher in laboratory tests than in real-world settings. In the lab, engineers control temperature, charge rates, and other variables. These ideal conditions help lithium-ion batteries reach round trip efficiency values close to 95%. Flow batteries can also show their best performance in the lab, sometimes reaching the upper end of their efficiency range.
When you move to field installations, the numbers can change. Outdoor temperatures, variable loads, and system integration all affect how much energy you actually recover. Lithium-ion batteries in the field usually deliver round trip efficiency between 85% and 90%. Flow batteries often operate in the 70% to 80% range in real-world projects. You should expect some difference between lab and field results because real systems face more challenges.
Note: Always check if efficiency numbers come from lab tests or actual field data. This helps you set realistic expectations for your own project.
Case studies
You can see how flow batteries perform in real-world projects by looking at several large-scale installations. These projects show how flow batteries support renewable energy and grid storage. The following table highlights some examples:
|
Case Study Name |
Capacity |
|---|---|
|
5 MWh Invinity VS3; 50 MWh lithium-ion |
|
|
Chappice Lake Solar-Storage |
8.4 MWh Invinity VS3 |
|
Viejas Resort & Casino |
10 MWh Invinity VS3 |
|
Spencer Energy |
8 MWh Invinity VS3 |
At the Energy Superhub Oxford, you find both flow and lithium-ion batteries working together. This hybrid approach lets the site balance high efficiency with long-duration storage. Other projects, like Chappice Lake and Viejas Resort & Casino, use flow batteries to store solar energy and provide backup power. These examples show that flow batteries can deliver reliable performance and help you meet your energy goals in real-world conditions.
Flow batteries often support projects that need long-duration storage and frequent cycling. You can use these case studies to guide your own decisions about energy storage.
User implications
Choosing based on efficiency
When you select a battery system, round trip efficiency shapes your total cost and system design. You want to get the most usable energy from every charge. Higher round trip efficiency means less energy lost, which saves you money over time. For grid-scale projects, even small differences in efficiency can lead to big changes in operating costs.
-
Round trip efficiency directly affects how much energy you lose during charging and discharging.
-
Lower energy losses mean lower operational expenses for large systems.
-
For example, a 50MW/50MWh battery system with 10% efficiency losses could cost you $250,000 each year if electricity costs $0.10 per kWh.
-
If you choose a battery with higher efficiency, you reduce these losses and improve your return on investment.
For home energy storage, you want a battery that gives you the most power back after charging. Lithium-ion batteries, especially Lithium Iron Phosphate types, often reach 90-95% round trip efficiency. This means you get more usable energy and lower your electricity bills. You should also consider the efficiency of the whole system, including inverters and battery management.
Tip: Always check the round trip efficiency rating before you buy a battery system. Higher efficiency means more savings and better performance.
Application-specific considerations
You need to match battery technology to your specific needs. If you run a grid or a business, flow batteries offer long-duration storage and stable operation. They usually reach about 75% round trip efficiency. This makes them suitable for storing energy over many hours or days, even if they lose a bit more energy than lithium-ion batteries.
-
Flow batteries work well for long-duration storage, supporting renewable energy and backup power.
-
Lithium-ion batteries excel in short-duration, high-power applications because they have higher round trip efficiency.
-
You can use lithium-ion arrays for quick energy discharge and fast response to peak demand.
-
Battery arrays with high efficiency help stabilize the grid and balance renewable energy sources.
You should consider how often you cycle the battery and how much energy you need to store. For frequent cycling and rapid discharge, lithium-ion batteries give you better results. For projects that need long-term, stable energy storage, flow batteries provide reliability and scalability.
Note: The right battery choice depends on your goals, budget, and how you plan to use stored energy. Efficiency plays a key role in making your system cost-effective and sustainable.
You will find that lithium-ion batteries usually deliver higher round trip efficiency, often reaching 90–95%, especially in short-duration, high-power applications. Flow batteries offer stable performance and long lifespans, making them ideal for long-term grid storage.
-
Choose lithium-ion batteries for rapid cycling and minimal energy loss.
-
Select flow batteries for consistent output over thousands of cycles.
Prioritize round trip efficiency when you want lower costs or need to reduce energy waste. Always balance efficiency with lifespan, safety, and environmental impact for the best results.
FAQ
What does round trip efficiency mean for battery systems?
Round trip efficiency shows how much energy you get back after charging and discharging a battery. Higher efficiency means less energy wasted. You save money and help the environment by choosing batteries with better round trip efficiency.
Why do lithium-ion batteries have higher round trip efficiency than flow batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries use advanced materials and cell designs. These features reduce energy loss during charging and discharging. You see higher round trip efficiency because lithium-ion batteries waste less energy as heat or through side reactions.
Can flow batteries compete with lithium-ion batteries for home energy storage?
Flow batteries work best for large-scale or long-duration storage. You may find lithium-ion batteries more suitable for home use because they offer higher efficiency and compact size. Flow batteries excel in grid and renewable energy projects.
How does battery efficiency affect your electricity costs?
Lower efficiency means you lose more energy during storage. You pay for extra electricity to make up for these losses. Choosing a battery with higher round trip efficiency helps you lower your electricity bills over time.